Conditions & Diseases
Deep Venous Thrombosis
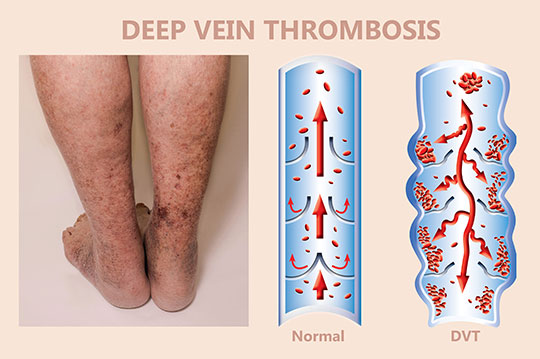
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but also can occur with no symptoms.
Deep vein thrombosis can develop if you have certain medical conditions that affect how your blood clots. It can also happen if you don’t move for a long time, such as after surgery or an accident, or when you’re confined to bed.
Deep vein thrombosis can be very serious because blood clots in your veins can break loose, travel through your bloodstream and lodge in your lungs, blocking blood flow (pulmonary embolism).
symptoms
- Swelling in your leg
- Pain in your leg
- Redness or discoloration of the skin on your leg
- A feeling of warmth in your leg
Treatment & Prevention
The mainstay of treatment of DVTs is blood thinners. However, some patients may have a contraindication to blood thinners, in these patients our surgeons can place an IVC filter. This filter will help catch any clot heading towards your lungs, so a pulmonary embolism (PE) does not occur. These filters are removable and can be removed when the patient can tolerate taking blood thinners.